[ad_1]
PORTLAND, USA, Jan 17 (IPS) – Yes, it’s unequivocally true: Americans are the most likely to be in the jailhouse now. The United States is the world’s leader in incarceration both in terms of the total number of people in prisons and jails and the rate of prisoners per capita.
The U.S. national incarceration rate, prisoners per 100,000 population, plainly stands out as the world’s highest at approximately 630. The countries with incarceration rates closest to the U.S. are Rwanda, Turkmenistan and El Salvador at around 575. The incarceration rate for the world at 140 as well as the rates for nearly all developed countries, in contrast, are a fraction of the United States rate (Figure 1).
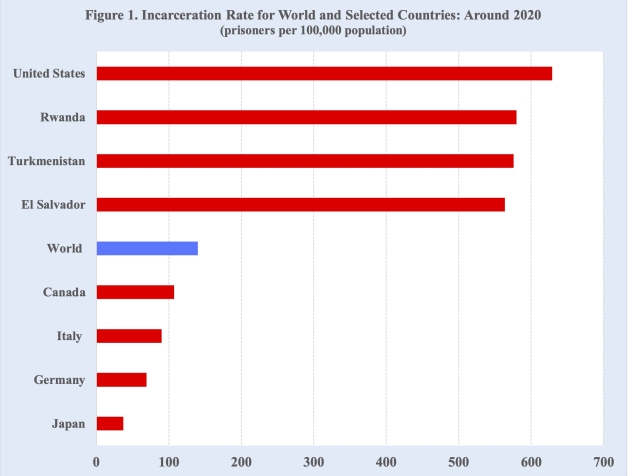
Moreover, the incarceration rates for the U.S. states are greater than those of most developed democracies. For example, the lowest state incarceration rate of 109 in Massachusetts is significantly greater than the rates for Denmark, Finland, France, Germany, Ireland, Italy, Japan, Netherlands, Norway, Sweden and Switzerland, which are below 90 prison inmates per 100,000 population.
The high incarceration rate is a relatively recent phenomenon for the United States. Between 1925 to 1975, for example, the U.S. incarceration rate was relatively stable at around 110 prisoners per 100,000 population. In the late 1970s the rate increased significantly, more than quadrupling since then, following the get tough on crime movement that swept across the country
Despite having slightly less than one-twentieth of the world’s population, the United States has approximately 20 percent of the world’s prison population. At the end of 2019 the number of prisoners held in the U.S. was the world’s largest at about 2.2 million.
That number of U.S. prisoners is about 10 percent lower than the peak level of inmates in prisons and jails of about 2.3 million in 2008. However, the current number of prisoners is substantially higher than it was in the mid 20th century. Fifty years ago, for example, the number of U.S. prisoners was 200,000, or close to 2 million less than it is today.
Following the United States in a distant second place is China with 1.7 million prisoners, or about 16 percent of the world total. It is followed by Brazil, India and Russia with approximately 0.8 million, 0.5 million and 0.5 million, respectively (Figure 2).
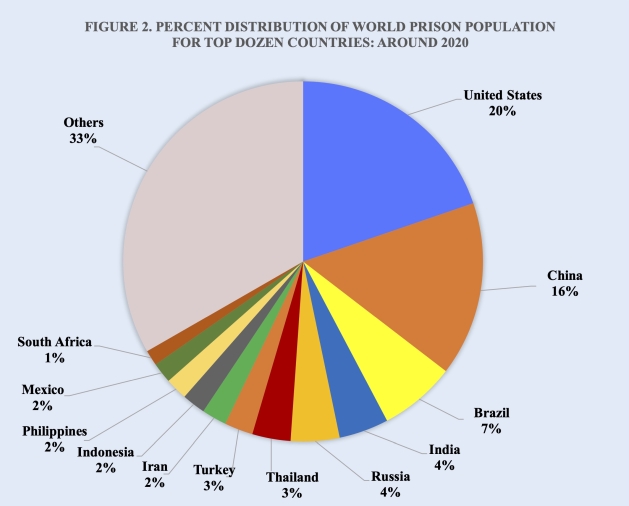
It is important to recognize that while the estimated total global prison population is over 11 million, that number is likely to be an underestimate of the world total. For example, if the numbers of underreported and political prisoners as well as those held in detention centers in various countries around the world, such as China, Eritrea, Indonesia, Myanmar, North Korea and Somalia, are included, the total worldwide prison population is believed to be more than 12 million.
In many parts of the world, prison populations are continuing to rise. For example, since the start of the 21st century, the prison populations have tripled in South America, more than doubled in south-eastern Asia and has nearly doubled in Oceania.
In the United States, in contrast, the number of prisoners in recent years has declined. The U.S. imprisonment rate in 2019 was at the lowest level since 1995. From 2009 to 2019, for example, the number of prisoners under state or federal jurisdiction dropped by 11 percent and the incarceration rate fell by 17 percent.
In some countries, including the U.S., the COVID-19 pandemic has also contributed to declines in prisoner numbers. Court operations, delays in trials and sentencing of persons led to a 40 percent decrease in admissions to U.S. state and federal prisons from 2019 and spurred a 25 percent drop in inmates held in local jails.
As is the case worldwide, the overwhelming majority of prisoners in the U.S. are males. In 2019, for example, females made up about 10 percent of those held in U.S. prisons and jails, or about 0.2 million, and constituted the highest female incarceration rate worldwide. Also, U.S. male prisoners are mostly under age 40, come from disadvantaged communities, are disproportionately minorities and often have drug and alcohol addictions.
U.S. incarceration rates also vary considerably by region and state. The states with the highest incarceration rates are typically located in the south. The top three states, for example, were Louisiana, Mississippi and Oklahoma, all with rates above 600 in 2019. In contrast, the three states with the lowest rates, all around 150 or less, were Massachusetts, Maine and Rhode Island.
At the end of 2019 slightly less than half, or about 46 percent, of sentenced federal prisoners were serving time for drug trafficking and 8 percent for a violent offense. Similarly among sentenced state prisoners, the most common offense was drug-related and about one out of seven, or 14 percent, were serving time for murder or manslaughter.
America’s high level of incarceration has raised various issues, including the civil rights of poor people and minorities, the crowded facilities with health risks and the financial strains on state budgets. Some contend that incarceration dehumanizes individuals, does little to increase public safety and is damaging to marginalized communities.
Also, many prisoners after being released encounter serious challenges. Among those challenges are reentering the labor force, finding suitable housing, reestablishing familial, social and community relationships, accessing public assistance and avoiding criminal activities.
Spending on prisons and jails also varies considerably across the United States. Those costs typically involve providing security, food, housing, recreation, education, maintenance and healthcare for prisoners.
The annual costs per inmate range from lows of below $20,000 in states such as Alabama, Kentucky and Oklahoma to highs of more than $50,000 in Connecticut, New Jersey and New York. Also, invariably across U.S. states, the annual costs of keeping an inmate imprisoned are significantly greater than government monies spent to educate an elementary/secondary school student in an academic year.
Various explanations or factors have been offered for why the United States has the world’s highest incarceration rate. Prominent among those explanations is the war on drugs, which over the years incarcerated a lot of people. Many experts contend that treatment for drug offenders would be a better option than incarceration.
Other factors and practices believed to contribute to the high U.S. incarceration rates include: harsher sentencing laws; longer prison sentences; greater likelihood of imprisonment; higher rates of violent crime; easily available firearms; a legacy of racial discrimination; the U.S. temperament; the lack of a social safety net; inadequate reentry services; employment discrimination; jail time for misdemeanors or low-level offenses; and the lack the funds to cover bail.
Also, most U.S. state judges and prosecutors are elected and consequently tend to be sensitive to public opinion about appropriate responses to crime. In contrast, criminal justice professionals in other developed countries are civil servants who are less likely to be pressured for lengthy jail time.
In sum, little disagreement exists about who are the most likely to be in the jailhouse now: residents of the United States. The reasons behind this lamentable incarceration achievement, however, are less indisputable. Also, the policies, changes and programs needed to address it remain contentious issues among U.S. elected officials, criminal justice professionals, law enforcement officers and the public.
Consequently, it seems that at least for the foreseeable future, the United States will retain its title as the world’s incarceration leader both in terms of the total number of people in prisons and jail and the rate of prisoners per capita.
* Joseph Chamie is a consulting demographer, a former director of the United Nations Population Division and author of numerous publications on population issues, including his recent book, “Births, Deaths, Migrations and Other Important Population Matters.”
© Inter Press Service (2022) — All Rights ReservedOriginal source: Inter Press Service
[ad_2]
Source link












